Learning adverbs and adverbial phrases is sometimes tricky, so teaching them!
Practice and learn all about adverbials with us. Our private English tutors have hands-on expertise in teaching such terms; here is the guide on adverbials. Give each line a read with a clear head and work on your grammar knowledge.
Definition of an Adverbial
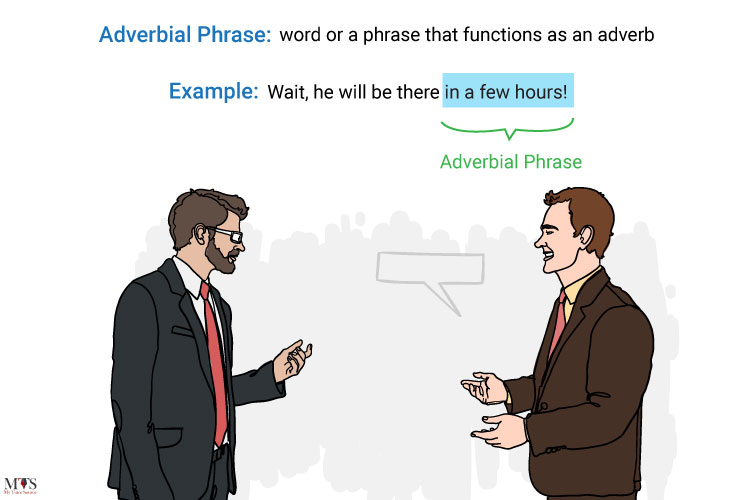
By definition, an adverbial is an adverb word or a phrase that functions as an adverb and typically expresses time, place, or manner. An adverbial gives you information about a verb like where, when, or how something happened.
Adverbials can be more than one word or phrase, which you can use in your daily speech to sound like a native English speaker. Adverbial phrases just add more information to your sentences. However, learning how or when to use them counts as a language skill.
For example
- Wait, he will be there in a few hours!
(Here, ‘in a few hours’ is an adverbial phrase)
- I prefer sitting in silence.
(Here, the adverbial phrase is ‘in silence’)
- They talk almost every day.
(Almost ‘every day’ is an adverbial phrase over)
Types of Adverbials with Examples
There are plenty of adverbials used in the English language, and each plays a slightly different role in making a sentence. Following are the main classes or types of adverbials:
1. Adverbial Complements
- It is a compulsory phrase, word, or clause to complete the meaning of a sentence.
- Sentences become grammatically wrong or meaningless when complements are removed.
Example of adverbial complements
- Your breakfast is on the table.
- He stayed in the hotel.
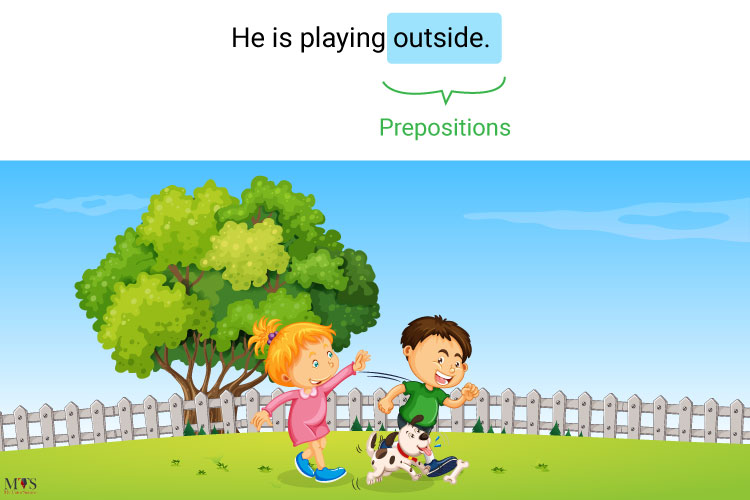
2. Prepositions
- These adverbials indicate the direction or location in a sentence, such as in or out / inside or outside.
Example of prepositions
3. Adjuncts
- These might be a part of the core meaning of sentences but not a must-have element either.
- Sentences still make sense without adjunct adverbials.
Example of adjuncts adverbials
- We are ready to leave for the party.
- John is studying with his friends.
4. Conjuncts
- These are the most used adverbial words.
- They link two phrases or sentences together; work as a conjunctive adverbial.
- Conjunct adverbial words are, however, still or therefore.
- Their existence might add meaning to the sentence, but their removal won’t affect the sentence’s grammatical structure.
Examples of conjunct adverbials
- This author is underrated. Still, I like to read his books.
- We went home late at night; therefore, we couldn’t make it on time.
5. Disjuncts
- These are used to make or add comments on the rest of the content or sentence.
- Such adverbials mostly stand outside the syntactic structure of a text. They help to declare the truthfulness of the particular statement to the reader or listener.
- Examples of disjunct adverbial phrases are hopefully, honestly, probably, frankly, and without a doubt.
- Removal of these words or phrases will not affect the grammatical structure or meaning of the sentence.
Examples of disjuncts adverbials
- Frankly, I’m not too fond of the system.
- Undoubtedly, he is a great teacher.
Note that, after removing the adverbial phrase, if the sentence’s meaning no longer makes sense or is changed, then the adverbial element is a complement. However, it is an adjunct if the intention is not altered or still intact.
Difference between an Adverb and an Adverbial
Adverbs and adverbials might sound similar, but they do slightly differ. Following are a few significant differences between adverbs and adverbials:
- Adverbs are the part of speech that modifies the verb, whereas adverbials tell how, when, why, or where something was done.
- Adverbials are the grammatical label that describes a function in a sentence.
- Adverbs are usually words like quietly, slowly whereas adverbials are the combination of words.
- An adverb can be used as an adverbial, but an adverbial cannot be used just as an adverb entirely.
- Adverbs mostly end with a suffix ‘ly’ added to the end of the word. For example: quickly, wildly, patiently, etc.
For example
- Adverb: James is incredibly smart.
- Adverbial: James thought the event went surprisingly well.
Format of Adverbial phrases
The three most common formats of adverbial phrases are:
1. Prepositional Phrase
Such adverbial phrases are headed by a preposition, e.g., in, near, from, by, on, with, etc. They also contain the object of a preposition and a modifier (if any).
For Example
- He is sitting in the dark.
- He stole money from an old lady’s bag.
2. Infinitive Phrase
The infinitive phrases contain an infinite form of a verb, modifier, and complement. An example of infinitive verbs is to play, go, jump, dig, etc.
For example
- Fill in the form to register yourself.
- He goes out to play.
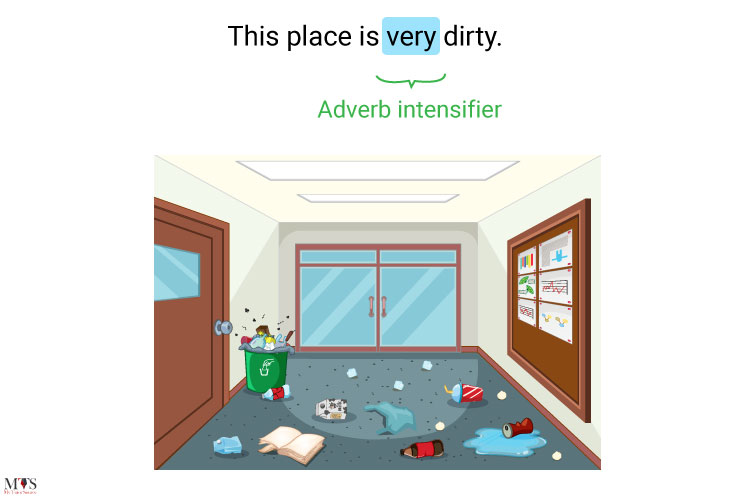
3. Adverb intensifier
- Adverbial phrases use an adverb with an intensifier. We use intensifiers quite a lot to strengthen or weaken another word.
- Very, really, barely, every, extremely are a few examples of intensifiers.
For example
- This place is very dirty.
- He is really good at designing.
More Examples of Adverbial Phrases
When (Time)
Below are the examples of adverbial phrases of time; they describe how long or often something happens:
- He goes to the gym every day.
- Hold on! I will do it in a minute.
- They usually go out on weekends.
- Before school, he goes for a walk.
Where (Place)
Below are the examples of adverbial phrases of place; they state direction, location, distance, or where something or someone is:
- She used to live nearby.
- Can I go out?
- It isn’t easy to get into the hut.
- I asked him to stand here.
How (Manner)
Following are the examples of adverbial phrases of manner, they state how something is done:
- He speaks English very well.
- Stop behaving in a silly way.
- He cried like a baby.
- He would always drive fast.
Why (Reason)
Here are a few adverbial phrase examples that state the reason of something like why it happened or was done:
- He stays up to study for exams.
- He went abroad to find a job.
- She cooked tasty food to impress her friends.
Conclusion
Here we are done with the basics of adverbial phrases, types, examples, and explanations. To learn more and practice exercises, book a tutoring session with our private English tutor right now! They will help you understand the concepts with structured and customized lessons. Our tutors’ strategies of teaching adverbs and adverbial phrases are quite clear and easy to understand, therefore, take some time and work with the best.
Find Top Tutors in Your Area
Find A Tutor